Introduction
Les problèmes esthétiques et électrochimiques des amalgames, la fragilité, la solubilité et la mauvaise biocompatibilité des silicates et des résines PMMA (Poly Méthyl MéthacrylAtes), ont conduit au développement d’un nouveau type de matériau dans les années 60 : les résines composites. Celles-ci ont donc été développées pour palier notamment les insuffisances esthétiques des obturations précédentes : Les silicates et les résines acryliques.
1953 : Bowen ajoute des charges de quartz aux résines époxy,
1955 : Buonocore introduit la notion de « mordançage »
1956 : Bowen crée le Bis-GMA (diméthacrylate glycidique de bisphénol A),
1962 : Bowen dépose le brevet du Bis-GMA.
Le nombre de résines composites n’a cessé d’augmenter depuis leur apparition et près de la moitié des publications des dix dernières années concernent ces matériaux. Une recherche conduite sur Internet concernant les résines composites, actuellement commercialisés, utilisées essentiellement en technique directe (tableau 1) mais aussi dans les reconstitutions corono-radiculaires et les scellements prothétiques, a permis d’en recenser 210, proposées par 42 fabricants.
Ce cours concerne uniquement les résines composites utilisées en technique directe.
| Fabricant | Composites | Famille | Viscosité | Mode de polymérisation |
| 3M ESPE | Concise | MA | M | Chémo |
| Filtek A110 | MI | M | Photo | |
| Filtek Flow | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Filtek P60 | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| Filtek Silorane | H – Min | C | Photo | |
| Filtek Supreme | H - MiN | M | Photo | |
| Filtek Z250 | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Z100 | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Alpha Dent | Alpha II AP | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| Alpha Flow | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Composite | H | M | Photo | |
| Core Build-Up | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| Core Build-Up | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Bisco | Aelite Anterior | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| Aelite All Purpose | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Aelite Flo | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Aelite Flo LV | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Aelite LS | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| BisFil 2 | H | C | Chémo | |
| BisFil 2B | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| BisCore | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| BisFil Core vs auto | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| BisFil Core vs photo | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Core-Flo | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| Light Core | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Pyramid | H | C | Photo | |
| Cavex | Quadrant Anterior Shine | H | M | Photo |
| Quadrant Core LC | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Quadrant Posterior Dense | H | C | Chémo | |
| Quadrant Universal LC | H | M | Photo | |
| Quadrant Unichem | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| Centrix | C-R | H (RCR) | Chémo | |
| Encore | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| Encore D/C | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| Encore SuperCure | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Versaflo | H | F | Photo | |
| Versalite | H | M | Photo | |
| Coltene Whaledent | Brilliant New Formula | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| Miris | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Para Core | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| Synergy Duo Shades | H | M | Photo | |
| Synergy Compact | H | C | Photo | |
| Synergy Flow | H | F | Photo | |
| Cosmedent | Renamel Flowable Hybrid | H - Mi | F | Photo |
| Renamel Flowable Microfill | MI | F | Photo | |
| Renamel Microfill | MI | M | Photo | |
| Renamel Posterior | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| Renamel Universal Microhybride | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Danville Materials | Starfill 2B | H (RCR) | Dual | |
| DenMat | Core Paste injectable | H (RCR) | Chémo | |
| Core Paste LC | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Core Paste syringeable | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| Flow Restore | H | F | Photo | |
| Virtuoso Flowable | H- MiN | F | Photo | |
| Virtuoso Packable | H- MiN | C | Photo | |
| Virtuoso Sculptable | MI | M | Photo | |
| Virtuoso Universal | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Dentoclic | Dentocore | H (RCR) | Dual | |
| Dentsply | Adaptic | H (RCR) | Chémo | |
| Ceram.X (Mono et Duo) | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Esthet.X | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Esthet.X Improved | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Quixfil | H | C | Photo | |
| Spectrum TPH | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Surefil | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| X Flow | H- MiN | F | Photo | |
| Discus | Matrixx Anterior Hybrid | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| Matrixx Anterior Microfill | MI | M | Photo | |
| Matrixx Posterior Hybrid | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| DMG | LuxaCore : chémo et dual | H (RCR) | Dual | |
| EDS | Ti-Core | H (RCR) | Chémo | |
| GC | Gradia Direct (Anterior et Posterior) | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| UniFil Flow | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Heraeus Kulzer | Charisma | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| Charisma F | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Charisma PPF | H - Mi | M | Chémo | |
| Durafil VS | MI | M | Photo | |
| Flowline | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Solitaire 2 | H | C | Photo | |
| Venus | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Venus Flow | H - MiN | F | Photo | |
| Ivoclar Vivadent | Artemis (Four Seasons) | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| Heliomolar | MIR | M | Photo | |
| Heliomolar Flow | MI | F | Photo | |
| Heliomolar HB | MIR | C | Photo | |
| Helioprogress | M | M | Photo | |
| Inten-S | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Multicore Flow | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| Multicore HB | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| Tetric | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Tetric Ceram | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Tetric Ceram HB | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| Tetric EvoCeram | H - MiN | M | Photo | |
| Tetric Flow | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Tetric Flow Chroma | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Jeneric Pentron | Alert | H | C | Photo |
| Build-It | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| Flow it | H | F | Photo | |
| Simile | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Kent Dental | Kentfil Anterior | H | M | Photo |
| Kentfil Posterior | H | M | Photo | |
| Kerr | Core Restore 2 | H (RCR) | Dual | |
| Herculite XRV | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Point 4 | H- Mi | M | Photo | |
| Point 4 Flowable | H- Mi | F | Photo | |
| Premise | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Prodigy | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Prodigy Condensable | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| Revolution 2 | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Kuraray | Clearfil AP-X | H | M | Photo |
| Clearfil Core | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| Clearfil Photo Anterior | MI | M | Photo | |
| Clearfil Photo Core | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Clearfil Photo Posterior | H | M | Photo | |
| Clearfil Posterior 3 | H | M | Chémo | |
| Clearfil ST | MI | M | Photo | |
| Lee Pharmaceuticals | Prosthodent | H (RCR) | Chémo | |
| Prosthodent VL pLus | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Micerium | Enamel Plus HFO | H- MiN | M | Photo |
| Enamel Plus HFO Flow | H- MiN | F | Photo | |
| Pulpdent | Flows-Rite | H | F | Photo |
| Hard Core | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| R&S | Lumifil | H | M | Photo |
| Southern Dental Industries | Glacier | H -Mi | M | Photo |
| Ice | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Rok | H - Mi | C | Photo | |
| Wave (3 viscosités) | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Sun Medical | Metafil AP | H | C | Photo |
| Metafil CX | MI | M | Photo | |
| Metafil Flo | H | F | Photo | |
| Tokuyama | Palfique Estelite | H- MiN | M | Photo |
| Palfique Estelite LV | H- MiN | F | Photo | |
| Ultradent | Amelogen Plus | H - Mi | M | Photo |
| Permaflo | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Permaflo DC | H - Mi / H (RCR) | F | Dual | |
| Voco | Admira | H - Mi (O) | M | Photo |
| Admira Flow | H - Mi (O) | F | Photo | |
| Arabesk Flow | H - Mi | F | Photo | |
| Arabesk Top | H - Mi | M | Photo | |
| Grandio | H- MiN | M | Photo | |
| Grandio Flow | H- MiN | F | Photo | |
| Polofil | H | M | Photo | |
| Polofil Molar | H (RCR) | Photo | ||
| Rebilda DC | H (RCR) | Dual | ||
| Rebilda SC | H (RCR) | Chémo | ||
| X-tra fil | H- Mi | C | Photo |
1 - Généralités
1 . 1 - Définitions
Un matériau composite est un matériau composé de plusieurs matériaux de nature ou d’origine différentes et dont les caractéristiques mécaniques sont supérieures à celles des matériaux entrant dans sa composition.
La condition fondamentale pour que cette définition soit valide, est que la cohésion de l’ensemble soit assurée par des liaisons mécaniques, physiques ou chimiques.
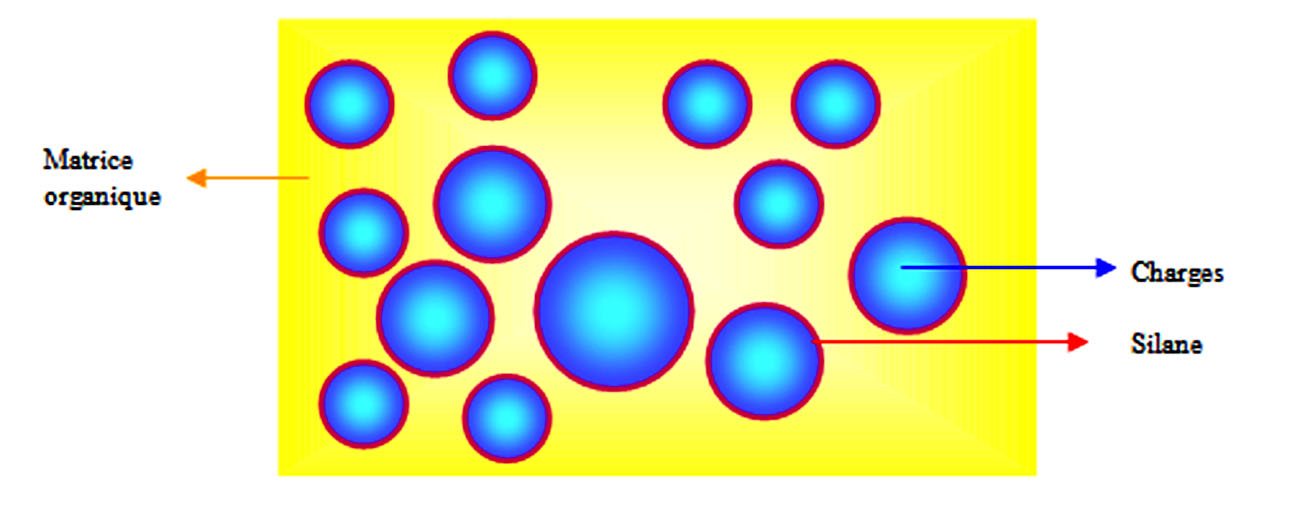
La plupart du temps ces matériaux sont constitués d’une matrice et d’un renfort (ex. de composites naturels : le bois et l’os).
En odontologie, on appelle RESINE COMPOSITE un matériau constitué d’une MATRICE ORGANIQUE RESINEUSE et d’un renfort constitué de CHARGES. La cohésion entre ces deux matériaux est assurée par un agent de couplage, un SILANE (Figure 1).